Contact Us Anytime! USA: +1 (551) 2485809 | India: 1800 102 1532 (Toll-Free) | Singapore: +65 6677 3658 | info@iarminfo.com
In the modern world we live in, medical devices are highly sophisticated with cloud sync, mobile apps, and other software capabilities, helping save lives and improving the quality of care provided to patients. But, as the saying goes, with great power comes great responsibility. This responsibility includes addressing potential vulnerabilities that could compromise device functionality or patient safety. Cybersecurity testing for connected medical devices has become a prerequisite rather than an extra step. It is conducted not only to safeguard patient safety but also to protect sensitive data.
As we know, the ceaseless growth in technology has resulted in medical hardware not being confined to the borders of being a stand-alone device. Hospital equipment has branched out greatly over the years; insulin pumps, and pacemakers, are now able to connect through a network. However, such additions give rise to the malicious threat of hacking.
Now consider a situation in which there is a cyber threat actor who can:
All these scenarios show the necessity of cybersecurity requirements to be considered throughout the life cycle of a medical device. Cybersecurity testing is carried out primarily to prevent such hacks and ensure trust in the MedTech business. It also makes sure that specific tools created with malicious intent are prevented or eliminated altogether.

This is one of the crucial parts in cybersecurity which pertains to employing automated systems to pinpoint possible vulnerabilities in the software, firmware, and network settings of a device. These scans are useful in discovering vulnerabilities at the earliest stages of the development cycle, when remediation can be done without impacting the project deadline.
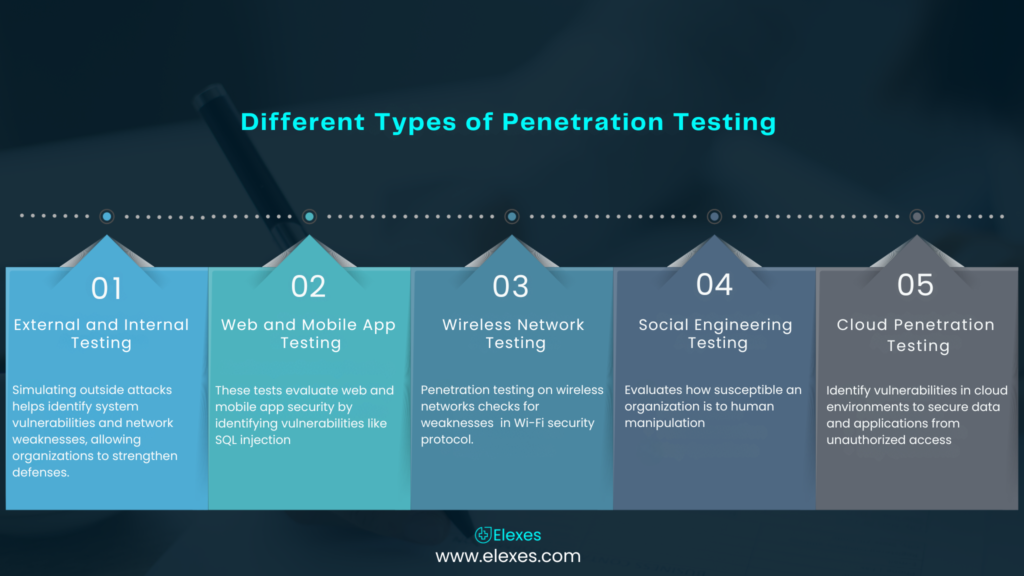
This type of testing mimics real-world cyberattacks that aim to target a medical device to evaluate its robustness. Ethical penetration testers do their best to penetrate the system by trying to find weaknesses. This simulates a scenario of what a malicious actor would do. Learn more about CREST certified penetration testing services.
Manufacturers perform vulnerability risk assessments to determine and estimate the probability and level of a specific cyber security threat. By performing such assessments, manufacturers would understand how to prioritize vulnerability and be able to effectively allocate required resources for implementing and executing risk mitigation measures.
Devices connected to hospital networks must undergo rigorous security testing to ensure they are well-protected against potential cyber threats. The process of security testing on a network confirms the protection and privacy of confidential information, secures and encrypts communication protocols, and restricts access to information systems within hospitals. It is very important to conduct these tests on the pre-defined network because it helps in the detection of weaknesses and in bolstering measures to avert hostility on the network.
The SAST method involves identifying possible security threats by performing a detailed audit and investigation of the code written into the medical device software. By using these steps, developers can appropriately minimize the amount of defects that would be present at the later stages of the development process.
DAST assesses a running application for vulnerabilities by simulating real-time attacks. It is a necessary step in finding issues that wouldn’t be immediately obvious in static testing.
To detect masked weaknesses such as crashes, buffer overflows, or other unusual behavior, fuzz testing blasts unexpected or poorly formatted inputs into the device. This form of testing increases resilience to unexpected circumstances.
Threat modeling evaluates the topology of a device, its data, and entry points for security threats. This systematic approach works for the teams assigned to the task because they’re better prepared for the risks.
Through this form of testing the appropriate application is tested in great detail and extensively for periods of high stress. Its critical importance in high-risk medical situations makes it essential for trustworthiness and safety.
While testing has a critical role to play in the cybersecurity of medical devices. It’s very important to be well aware of the best practices to ensure the security of medical devices. Here are some time tested practices.
✔ Risk Assessments – Identifying vulnerabilities and potential threats
✔ Mitigation Strategies – Implementing security controls to reduce risks
✔ Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) – Tracking third-party components
✔ Post-Market Surveillance – Monitoring and responding to emerging threats
Our expert documentation services ensure your cybersecurity measures are audit-ready, regulatory-compliant, and tailored to meet global standards. Read more about expert documentation services.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Medical Devices as you may have guessed will be dynamic, cybersecurity threats also keep changing with evolving technology. AI-enabled threat detection systems, blockchain technology for secure data management, and better cooperation between manufacturers and regulators would be revolutionizing safety of features in medical devices.
Testing connected medical devices in terms of cybersecurity is critical and life-saving. Best practices should be rigorously followed and must be continuously updated and revisited to stay on track with the advancements in the medical device industry.
We ensure your medical devices undergo rigorous and comprehensive testing, delivering the highest standards of quality and safety, with the expert support of our trusted partner, Elexes, all necessary documentation is seamlessly prepared and readily provided to streamline your journey toward critical marketing approvals—such as FDA clearance, CE Mark certification, and more. Together, we pave the way for your success in the global MedTech market.
As CEO of Elexes, Parul Chansoria, said: “A cyber breach in healthcare can cost more than money—it can cost lives”
Let’s secure the present so that we can build a better and more secure future for the patients and healthcare systems!
Guest Post – This blog is written by our trusted partner, Elexes, a global leader in regulatory and quality compliance consulting. Elexes supports medical device, SaMD, and IVD companies worldwide both at the premarket and postmarket stages.
We’re here to assist you! Send us a message and learn how our team can support your needs.
